Equal employment Opportunity definition and historical context
Equal employment opportunity definition:
Equal employment opportunity in HRM refers to the principles and practices that ensure fairness, inclusivity, and unbiased treatment in the workplace, regardless of an individual’s race, gender, age, disability, or other protected characteristics.
These opportunities are crucial in promoting diversity and creating an environment where every employee can thrive and contribute to their fullest potential.
The historical context of equal employment opportunity
The quest for equal employment opportunity can be traced back to the early 20th century, when marginalized groups, such as women and racial minorities, began demanding fair treatment and access to employment.
Over time, societal progress and legal reforms have helped shape the landscape of workplace equality, leading to the establishment of legislation and frameworks that prioritize diversity and inclusion.

Table of Contents
Equal Employment Opportunity Act
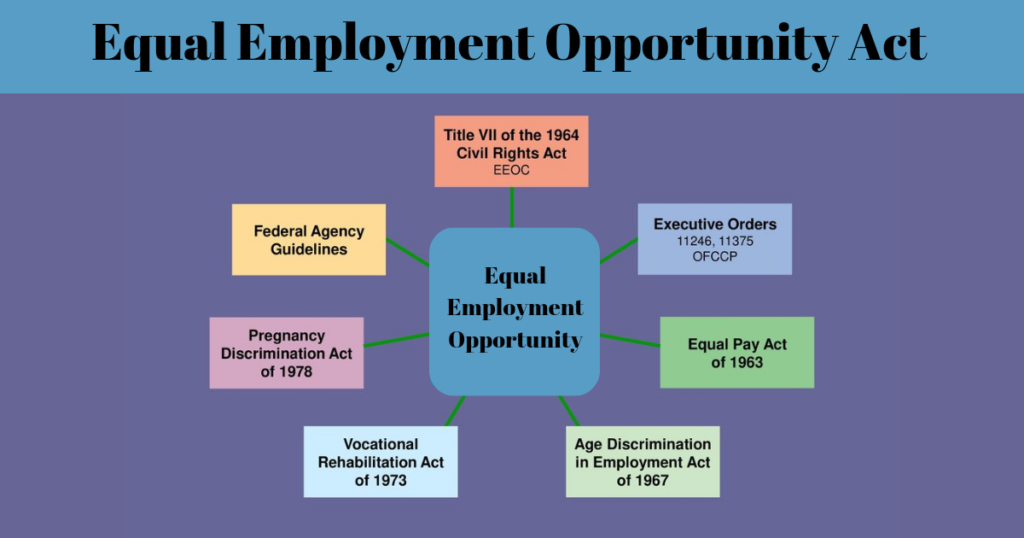
Legislation and Legal Framework
A. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 is a landmark legislation that prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. It serves as the foundation for promoting equal employment opportunities and has had a profound impact on breaking down barriers and promoting diversity in the workforce.
B. The Equal Pay Act of 1963
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 addresses the issue of gender-based wage discrimination by requiring that men and women receive equal pay for equal work performed. It has played a crucial role in narrowing the gender pay gap and ensuring that women are compensated fairly for their contributions.
C. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a comprehensive legislation that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in various aspects of employment, including recruitment, hiring, promotion, and workplace accommodations. It aims to ensure equal opportunities for individuals with disabilities to participate fully in the workforce.
D. Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) safeguards individuals who are 40 years or older from age-related discrimination in employment. It promotes fairness and equal opportunities by prohibiting employers from making employment decisions based on an individual’s age.
E. Affirmative Action initiatives
Affirmative Action initiatives are policies aimed at addressing historical imbalances and promoting diversity in the workplace. These initiatives encourage employers to take proactive measures to recruit, hire, and promote individuals from underrepresented groups. The goal is to create a more inclusive environment that embraces the benefits of diverse perspectives and experiences.
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is a federal agency in the United States responsible for enforcing laws related to workplace discrimination and ensuring equal employment opportunities for all individuals. Here is a short note on the EEOC:

Role and Mission:
The EEOC was established in 1965 as part of the Civil Rights Act. Its primary mission is to enforce federal laws that prohibit workplace discrimination based on an individual’s race, color, religion, sex (including pregnancy, gender identity, and sexual orientation), national origin, age, disability, or genetic information. The agency aims to create a fair and inclusive work environment where everyone has an equal opportunity to succeed, regardless of their background.
Key Responsibilities:
- Investigation: The EEOC investigates complaints of discrimination filed by individuals against employers. These complaints can encompass a wide range of issues, from hiring and firing practices to workplace harassment and wage disparities.
- Education and Outreach: The EEOC conducts educational programs and outreach initiatives to raise awareness about workplace discrimination and employees’ rights. They provide guidance to employers and employees about how to prevent discrimination and promote inclusivity.
- Litigation: When necessary, the EEOC can file lawsuits against employers on behalf of individuals or groups who have experienced discrimination. These legal actions aim to remedy discriminatory practices and secure compensation for victims.
- Policy Development: The EEOC plays a role in shaping policies related to equal employment opportunity. They provide input and guidance to lawmakers and government agencies to strengthen anti-discrimination laws and regulations.
Significance:
The EEOC is a crucial organization in the United States because it helps ensure that workplaces are free from discrimination and harassment. By investigating complaints, providing education, and taking legal action when needed, the EEOC promotes diversity, inclusivity, and equal opportunities in the job market. Its work contributes to creating a fair and just society where individuals can pursue their careers without facing discrimination based on their protected characteristics.
Equal employment opportunity act of 1972
The Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972 (EEOA) is a significant piece of legislation in the United States that amended and expanded the existing anti-discrimination framework established by the Civil Rights Act of 1964. The EEOA aimed to address certain limitations in the original act and enhance the protection of individuals against discrimination in employment. Here are some key aspects of the Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972:
Background:
The Equal Employment Opportunity Act in Human Resource Management was enacted in 1972 as an amendment to the Civil Rights Act of 1964. It was a response to growing concerns about discrimination in the workplace based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. The EEOA was designed to provide additional legal tools to combat employment discrimination and promote equal opportunities for all individuals.
Key Provisions:
- Expansion of Coverage: The EEOA expanded the scope of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 by extending its anti-discrimination provisions to include not only public and private employers but also labor unions and employment agencies. This broader coverage ensured that various entities involved in the employment process were held accountable for discriminatory practices.
- Sex-Based Discrimination: One of the pivotal changes introduced by the EEOA was the prohibition of sex-based discrimination in employment. While the Civil Rights Act of 1964 originally focused on race, color, religion, and national origin, the EEOA explicitly included sex as a protected category. This laid the foundation for addressing gender-based discrimination and harassment in the workplace.
- Enforcement Authority: The EEOA strengthened the enforcement authority of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the federal agency responsible for enforcing anti-discrimination laws. It provided the EEOC with more power to investigate complaints of discrimination and take legal action against employers or entities engaged in discriminatory practices.
- Affirmative Action: The EEOA allowed for the continuation of affirmative action programs designed to address historical imbalances in the workforce. These programs aimed to promote diversity and equal opportunities by taking proactive measures to remedy past discrimination.
- Bilingual Regulations: The EEOA required federal agencies to implement regulations that addressed the needs of individuals who were not proficient in English. This helped ensure that language barriers did not become a source of discrimination in employment.
- Whistleblower Protections: The act provided protections for employees who reported discriminatory practices in their workplace. Employers were prohibited from retaliating against individuals who filed complaints or testified in discrimination cases, encouraging employees to come forward without fear of reprisal.
- Expanded Remedies: The EEOA expanded the remedies available to individuals who experienced discrimination, including back pay, compensatory damages, and injunctive relief.
Impact:
The Equal Employment Opportunity Act in Human Resource Management has had a profound impact on the U.S. workplace. It significantly strengthened the legal framework for combating discrimination and promoting equal employment opportunities. By recognizing and addressing issues like sexual harassment and expanding enforcement powers, the EEOA has played a crucial role in advancing workplace equality.
This act reflects the ongoing commitment of the United States to the principles of fairness, inclusivity, and equal opportunity in employment. It has been instrumental in shaping workplace practices, fostering diversity, and ensuring that all individuals have a level playing field in pursuing their careers, regardless of their race, gender, religion, or other protected characteristics.
Key Components of Equal Employment Opportunity
A. Non-discrimination policies
Non-discrimination policies serve as the foundation for equal employment opportunity. They explicitly state that no employee or job applicant shall be treated unfairly or disadvantaged due to protected characteristics. Such policies foster inclusivity and create a safe and welcoming environment for all employees.
B. Fair hiring practices
Fair hiring practices involve ensuring that recruitment processes are equitable and free from bias. Employers should focus on qualifications, skills, and experience as the basis for hiring decisions, rather than relying on unconscious biases. This approach allows for a diverse pool of talent and opportunities for underrepresented individuals.
C. Anti-harassment policies
Anti-harassment policies are essential in creating a respectful work environment. These policies prohibit any form of harassment, including verbal, physical, or psychological, based on protected characteristics. By fostering a culture of respect, companies can nurture a diverse workforce and prevent discriminatory behaviors.
D. Accessibility and accommodation provisions
Equal employment opportunity also encompasses providing accessibility and reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities. Companies should ensure that their workplaces are physically accessible, and reasonable adjustments are made to accommodate employees with disabilities, allowing them to perform their duties effectively.
E. Pay equity and transparency
Promoting pay equity and transparency is critical in achieving equal employment opportunity. Companies should regularly assess their compensation structures, identifying any gender, racial, or other disparities, and take necessary actions to rectify them. Transparent reporting and communication regarding pay scales can also promote fairness and equality.
Challenges in Achieving Equal Employment Opportunities

A. Implicit bias and stereotypes
One of the primary challenges in achieving equal employment opportunity is the presence of implicit bias and stereotypes. These unconscious biases can influence decision-making processes, leading to discriminatory practices. Overcoming these biases requires awareness, education, and continuous effort to recognize and challenge assumptions.
B. The gender pay gap
Despite legislative efforts, the gender pay gap remains a significant challenge. Women, on average, earn less than their male counterparts for performing similar work. Addressing this disparity requires organizations to implement pay equity policies, eliminate gender biases in performance evaluations, and promote a culture of equal opportunities for career progression.
C. Workplace harassment and discrimination
Instances of workplace harassment and discrimination pose significant obstacles to equal employment opportunity. Creating a culture where employees feel safe and respected requires robust anti-harassment policies, swift action on complaints, and conducting regular training programs to improve awareness and prevent discriminatory behaviors.
D. Limited representation in leadership roles
Another obstacle to equal employment opportunities is the limited representation of underrepresented groups in leadership roles. This lack of diversity often perpetuates biases and prevents the full inclusion of different viewpoints and experiences. Intentional efforts to develop diverse talent pipelines, mentorship programs, and leadership development initiatives can help break these barriers.
E. Disparities faced by marginalized groups
Marginalized groups, including racial and ethnic minorities, individuals with disabilities, and LGBTQ+ individuals, often face unique challenges in accessing and advancing in employment opportunities. Overcoming these disparities requires organizations to implement targeted initiatives, create safe spaces, and foster an inclusive environment.
Corporate Social Responsibility in Equal Employment Opportunity
A. Transparent reporting and accountability
Corporate social responsibility entails transparent reporting and accountability regarding diversity and inclusion efforts. Companies should regularly disclose data on representation, pay equity, and progress made towards achieving equal employment opportunity. This transparency holds organizations accountable to their commitments.
B. Corporate initiatives for social impact
In addition to internal initiatives, corporations can have a broader societal impact by supporting external programs that promote equal employment opportunity. This can include partnerships with nonprofit organizations, funding scholarships, or investing in initiatives that empower underrepresented communities.
C. Collaboration with community organizations
Collaborating with community organizations is key to building strong relationships and addressing specific challenges faced by underrepresented individuals. By partnering with these organizations, corporations can gain insights, leverage resources, and contribute to the improvement of equal employment opportunity.
Global Perspectives on Equal Employment Opportunity in HRM
A. Contrasting international approaches to equal opportunity laws
Different countries have varying approaches to equal opportunity laws and regulations. Comparative analyses can highlight the strengths and weaknesses of these approaches, providing valuable insights for policymakers and organizations striving for global equal employment opportunities.
B. Case studies of successful global equal employment initiatives
Exploring successful global equal employment initiatives can inspire organizations to adopt innovative practices. Case studies from different regions can showcase diverse strategies that have achieved remarkable results, encouraging cross-cultural learning and adaptation.
C. The role of international collaborations
International collaborations play an essential role in advancing equal employment opportunity on a global scale. Governments, organizations, and NGOs can collaborate to exchange best practices, advocate for changes in policies, and drive meaningful progress across borders.
Initiatives and Best Practices

A. Employee resource groups (ERGs)
Employee resource groups (ERGs) are voluntary, employee-led groups that create spaces for networking, support, and professional development. ERGs promote diversity, provide a platform for underrepresented individuals to share experiences, and contribute to an inclusive workplace culture.
B. Diversity training and awareness programs
Diversity training and awareness programs help educate employees about biases, stereotypes, and the importance of fostering inclusivity. By increasing awareness and providing tools to address these biases, organizations can build a more inclusive work environment.
C. Mentoring and sponsorship programs
Mentoring and sponsorship programs pair underrepresented individuals with experienced professionals who can provide guidance and support. These programs can help cultivate talent, increase diversity in leadership roles, and create a culture of advancement and inclusion.
D. Flexible work arrangements
Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options, flexible hours, and job sharing, can benefit individuals with caregiving responsibilities or those needing accommodations. Such arrangements promote work-life balance and help organizations attract and retain a diverse workforce.
E. Supplier diversity programs
Supplier diversity programs encourage organizations to engage a diverse range of suppliers. By actively seeking out and supporting businesses owned by underrepresented individuals, companies can contribute to the economic growth and empowerment of marginalized communities.
Future Outlook and Trends
A. The impact of emerging technologies on equal employment opportunity
Emerging technologies present both opportunities and challenges for achieving equal employment opportunities. As artificial intelligence and automation become more prevalent, organizations must ensure that these technologies are designed and implemented in a way that does not perpetuate biases and unfair practices.
B. Incorporating diversity and inclusion in remote work settings
The rise of remote work has brought new considerations for promoting diversity and inclusion. Organizations need to adapt their strategies to ensure remote employees have equal access to opportunities, are included in decision-making processes, and receive the necessary support to thrive in remote work settings.
C. Shaping the workforce of tomorrow
The pursuit of equal employment opportunities goes hand in hand with shaping the workforce of tomorrow. By embracing diversity, organizations can harness the potential of all individuals, nurture talent, and create a future workforce that truly represents the communities they serve.
Summary
Equal employment Opportunity is crucial for creating diverse, inclusive, and fair workplaces. These opportunities promote innovation, enhance productivity, and cultivate a work environment where every individual feels valued and respected.
FAQs
A. What is equal employment opportunity?
Equal employment opportunity refers to the principles and practices that ensure fairness, inclusivity, and unbiased treatment in the workplace, regardless of an individual’s protected characteristics.
B. How can companies promote diversity and inclusion?
Companies can promote diversity and inclusion by implementing non-discrimination policies, fair hiring practices, anti-harassment policies, and providing accessibility and accommodations. They can also foster inclusivity through diversity training, mentorship programs, and employee resource groups.
C. What challenges hinder the achievement of equal employment opportunities?
Challenges in achieving equal employment opportunities include implicit bias, the gender pay gap, workplace harassment and discrimination, limited representation in leadership roles, and disparities faced by marginalized groups.
D. What are some successful examples of equal employment initiatives?
Successful examples of equal employment initiatives include implementing mentorship and sponsorship programs, incorporating flexible work arrangements, and partnering with community organizations to provide support and opportunities for underrepresented groups.
E. How can individuals contribute to equal employment opportunities?
Individuals can contribute to equal employment opportunities by recognizing and challenging their own biases, advocating for inclusive practices within their organizations, and supporting initiatives that promote diversity and inclusion in their communities.