Introduction to Job Analysis
Job analysis is a fundamental process in human resource management that involves a systematic examination of various job-related aspects to gain a comprehensive understanding of the nature and requirements of a specific job role.
It involves collecting, analyzing, and documenting information about the tasks, responsibilities, skills, qualifications, and work environment associated with a job.
This process serves as a foundation for several critical HR activities, making it an indispensable tool for organizations.
The Role of Job Analysis in HR Management
Establishing job requirements and specifications
Job analysis plays a crucial role in clearly defining job requirements and specifications. By identifying the essential tasks, responsibilities, and qualifications for a particular job, organizations can develop accurate job descriptions and person specifications. This ensures that candidates possess the necessary skills and qualifications to perform the job effectively.
Enhancing recruitment and selection processes
Effective recruitment and selection processes heavily rely on the findings of job analysis. By understanding the key competencies and qualifications required for a job, organizations can design targeted job advertisements, screen candidates more efficiently, and conduct focused interviews. This improves the overall quality of new hires and reduces turnover.
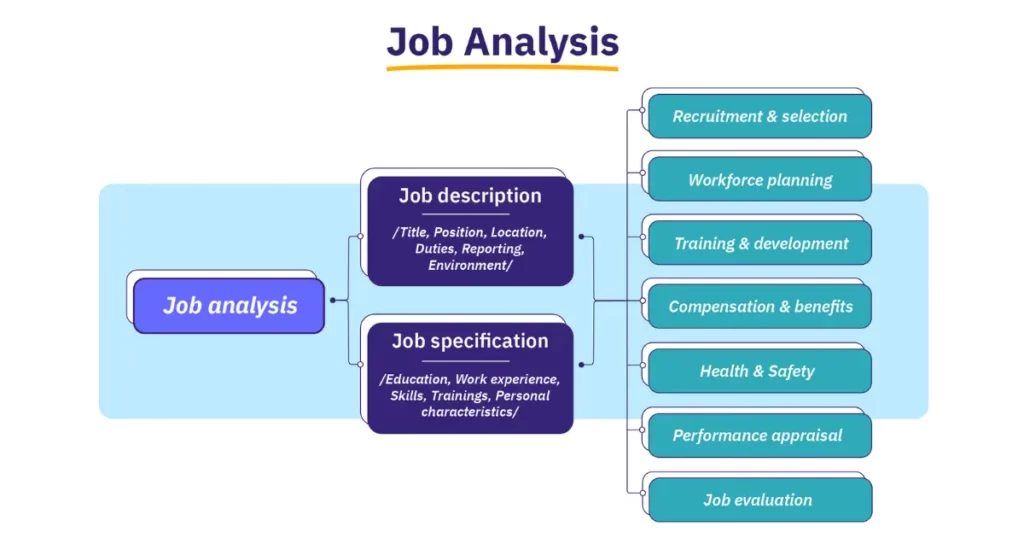
Table of Contents
Facilitating performance management
Job analysis provides a solid foundation for performance management. By clearly defining job expectations, organizations can establish performance standards and objectives that align with job requirements. Additionally, it helps identify key performance indicators and sets benchmarks for evaluating employee performance, enabling organizations to provide constructive feedback and implement performance improvement initiatives.
Supporting training and development initiatives
Organizations utilize job analysis findings to identify skill gaps and training needs within their workforce. By understanding the skills, competencies, and qualifications required for a job, training programs can be designed to enhance employees’ capabilities and align them with job requirements. This ensures a skilled and competent workforce that can meet organizational goals effectively.
Enabling fair compensation and benefits strategies
Job analysis serves as a basis for developing fair and equitable compensation and benefits strategies. By understanding the level of responsibility, required qualifications, and skill requirements of a job, organizations can establish appropriate salary ranges and incentive structures. This helps in attracting and retaining top talent while ensuring internal equity.
The Job Analysis Process
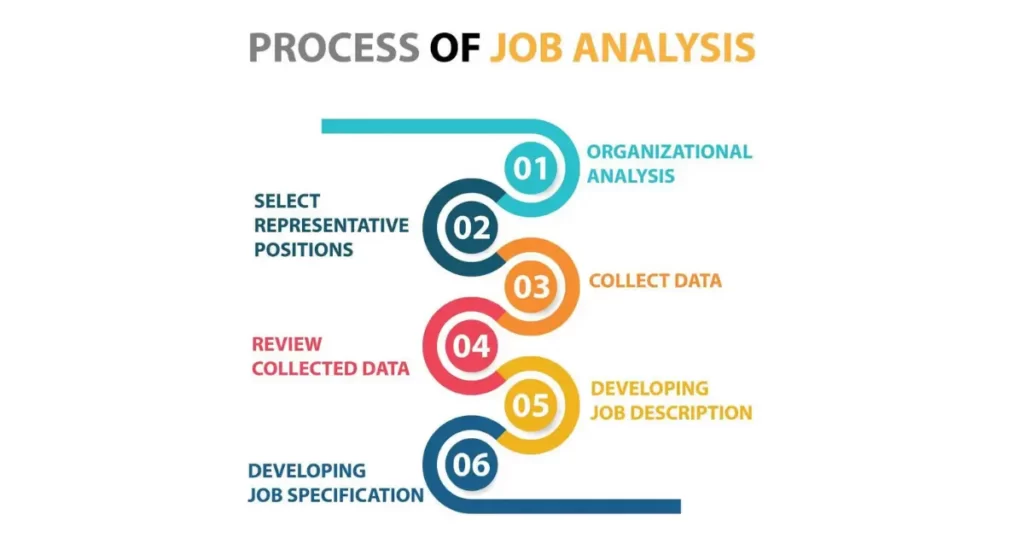
Identifying job analysis methods
Several methods can be employed to conduct job analysis, including observation, interviews, questionnaires, and task analysis. Organizations can choose the most suitable method based on their specific requirements and available resources.
Collecting job data through interviews and questionnaires
The collection of job data is a critical step in the job analysis process. This can be accomplished through structured interviews with job incumbents, supervisors, and subject matter experts. Additionally, questionnaires can be distributed to gather information about the specific tasks, responsibilities, and competencies associated with a job.
Analyzing job data and creating job descriptions
Once the data is gathered, it is essential to analyze and synthesize the information obtained. This involves examining the collected data and identifying common patterns, key tasks, and required qualifications. The results of this analysis are used to create accurate and detailed job descriptions that provide a clear understanding of the job role.
Conducting job evaluations and assessments
Job evaluations and assessments are conducted to determine the relative worth of different jobs within an organization. By comparing job requirements, skills, responsibilities, and qualifications, organizations can establish a hierarchy and develop appropriate compensation and career progression frameworks.
Key Components of Job Analysis

Job tasks and responsibilities
The primary focus of job analysis is to identify and document the specific tasks and responsibilities associated with a job. This includes understanding the frequency, complexity, and importance of each task, as well as any specific tools or technologies utilized.
Required skills, qualifications, and competencies
Job analysis helps identify the essential skills, qualifications, and competencies required for a particular job role. This includes both technical and non-technical skills, educational requirements, certifications, and any other qualifications necessary to perform the job effectively.
Work environment and conditions
An in-depth understanding of the work environment and conditions associated with a job is crucial for job analysis. This includes factors such as physical demands, work schedule, working conditions, and any potential hazards or risks.
Relationships and interactions within the job
Job analysis also examines the relationships and interactions a job has with other roles within the organization. This includes understanding reporting structures, collaboration requirements, and communication channels, which helps create clarity and streamline workflow processes.
Job Analysis Techniques
Task-based analysis
Task-based analysis focuses on identifying and understanding the specific tasks and responsibilities associated with a job. This involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller components and analyzing the skills and knowledge required to perform each task effectively.
Behavioral analysis
Behavioral analysis emphasizes observing and understanding the behaviors, actions, and interactions of individuals performing a job. This technique provides insights into the soft skills, attitudes, and interpersonal dynamics necessary for success in a particular role.
Competency-based analysis
Competency-based analysis focuses on identifying the core competencies required for a job. This includes both technical and behavioral competencies, such as problem-solving abilities, communication skills, and leadership qualities.
Job-oriented analysis
Job-oriented analysis takes a holistic approach to job-analysis by considering various job-related factors, including tasks, responsibilities, skills, qualifications, and work environment. This technique provides a comprehensive understanding of a job and helps establish effective HR strategies.
Job description and job specification
“Job description” and “job specification” are essential components of the human resource management process that help define and manage job roles within an organization:
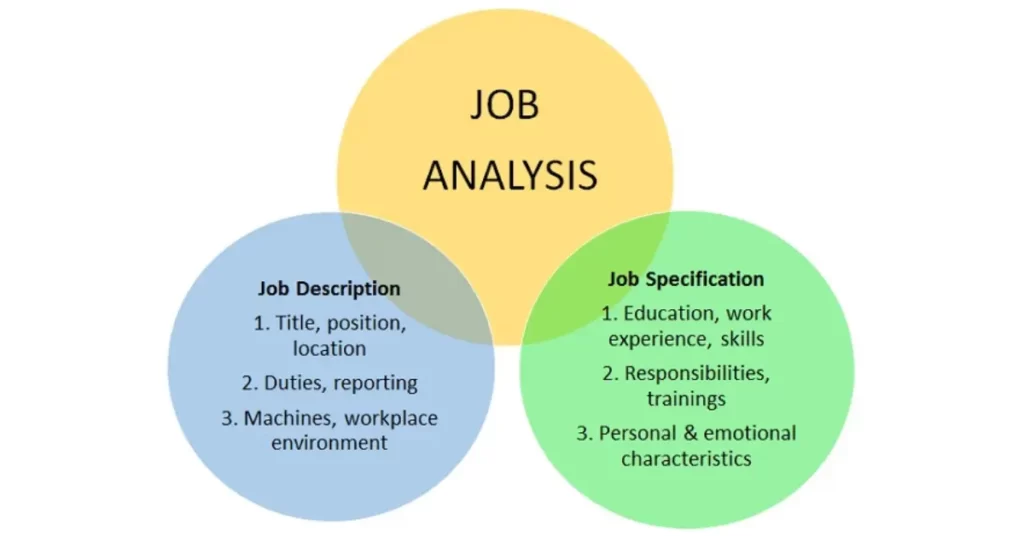
Job Description:
- Definition: A job description is a detailed document that outlines the specific tasks, responsibilities, duties, and requirements associated with a particular job position within an organization.
- Purpose: It serves as a comprehensive guide for both employees and employers. For employees, it clarifies what is expected of them in their roles. For employers, it aids in recruitment, performance evaluation, and legal compliance.
- Contents: A typical job description includes job title, job summary, key responsibilities, qualifications, skills, experience, working conditions, and reporting relationships.
Job Specification:
- Definition: A job specification is a document that details the qualifications, skills, and attributes required of a person to perform a specific job effectively. It provides a profile of the ideal candidate.
- Purpose: Job specifications are used in the recruitment and selection process to identify the most suitable candidates for a particular position. They help in aligning candidate qualifications with job requirements.
- Contents: A job specification typically includes educational qualifications, experience, skills, knowledge, physical requirements, and any special certifications or licenses needed for the job.
In summary, a job description outlines what a job entails in terms of tasks and responsibilities, while a job specification defines the qualifications and attributes necessary for an individual to perform that job successfully. Together, these documents play a crucial role in human resource management, from recruitment and selection to performance evaluation and employee development.
Challenges in Job Analysis
Obtaining accurate and reliable data
Accurate and reliable data collection can be a significant challenge in job analysis. Depending on the method chosen, there may be biases, inconsistencies, or incomplete information. HR professionals must employ rigorous data collection techniques and ensure the credibility of the data obtained.
Balancing standardization with flexibility
Job analysis requires balancing the need for standardized job roles with the flexibility to adapt to evolving organizational needs. This can be challenging, as organizations must strive to maintain consistency while allowing for necessary adjustments.
Incorporating evolving job roles and technologies
The dynamic nature of jobs, especially in rapidly changing industries, poses a challenge in job analysis. New job roles and technologies emerge constantly, requiring HR professionals to adapt their job-analysis techniques and keep up with evolving job requirements.
Methods of Job Analysis
“Methods of job analysis” are the various approaches and techniques used to gather information about a specific job within an organization. These methods help in understanding the duties, responsibilities, qualifications, and requirements of a job role. Here are some common methods of job analysis:

- Observation: This method involves directly observing employees as they perform their job tasks. It provides firsthand insight into what the job entails, but it can be time-consuming and may not capture all aspects of the job.
- Interviews: Job analysts can conduct structured interviews with employees, supervisors, and managers to gather information about job duties, skills, and requirements. This method allows for in-depth conversations but may be subject to bias or incomplete information.
- Questionnaires and Surveys: Job analysis questionnaires and surveys are distributed to employees and supervisors to collect data about job tasks, responsibilities, and required qualifications. These can be standardized and efficient but may have response bias.
- Job Diaries/Logs: Employees maintain records or diaries of their activities over a specified period. This method provides detailed information about daily tasks but may be burdensome for employees.
- Critical Incident Technique: This approach focuses on specific events or situations that are critical to job performance. It helps identify key job tasks and behaviors that lead to success or failure.
- Job Analysis Panels (Group Interview): A group of subject matter experts, including employees and supervisors, come together to discuss and document job-related information. This method combines multiple perspectives but can be time-intensive.
- Functional Job Analysis: This method categorizes jobs based on the interaction of people, data, and things. It helps in understanding the core elements of a job’s function.
- Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ): A standardized questionnaire with a comprehensive list of job elements is used to evaluate job characteristics. It’s useful for comparing different jobs within an organization.
- Job Shadowing (Record Method): An analyst spends time with an employee to observe and understand their daily tasks, responsibilities, and challenges. It provides a detailed view of the job but may disrupt regular work.
- Work Sampling: This technique involves random sampling of an employee’s activities over a period, providing data on the distribution of work tasks.
Job Analysis Importance
Enhanced organizational performance
By aligning job roles with organizational goals and requirements, job analysis contributes to enhanced organizational performance. It ensures that each position is optimized to support the achievement of strategic objectives.
Improved employee productivity and effectiveness
Through job-analysis, organizations can better understand the skills and qualifications necessary for each job, resulting in improved employee productivity and effectiveness. This reduces errors, enhances efficiency, and increases overall job satisfaction.
Better alignment of talent with job requirements
Job-analysis helps organizations identify the specific skills, qualifications, and competencies required for each job role. This enables them to align their talent acquisition and development strategies with job requirements, resulting in a workforce that is better suited to meet organizational goals.
Job Analysis in the Digital Era
Impact of technology on job-analysis
Technology has revolutionized job-analysis processes, enabling faster data collection, analysis, and documentation. Online platforms, data analytics tools, and AI-powered software have made job analysis more efficient and accurate.
Leveraging AI and automation in job-analysis processes
AI and automation have the potential to revolutionize job analysis by automating data collection, analyzing large datasets, and identifying patterns and trends. This can lead to faster and more accurate job-analysis outcomes.
FAQS
What is the difference between job analysis and job evaluation?
Job analysis focuses on understanding and documenting the tasks, responsibilities, skills, and qualifications associated with a job. Job evaluation, on the other hand, determines the relative worth or value of different jobs within an organization to establish appropriate compensation frameworks.
Can job analysis be applied to all job roles?
Yes, job analysis can be applied to all job roles, regardless of the level or complexity. However, the depth and complexity of the analysis may vary depending on the nature of the job.
How often should job analysis be conducted?
Job analysis should be conducted periodically to ensure that job requirements and specifications remain accurate and up-to-date. The frequency may vary depending on factors such as organizational changes, technological advancements, and evolving job roles.
What are the potential challenges in implementing job analysis?
Some potential challenges in implementing job analysis include obtaining accurate and reliable data, balancing standardization with flexibility, and incorporating evolving job roles and technologies. Strategies such as rigorous data collection, stakeholder involvement, and continuous evaluation can help overcome these challenges.
Is job analysis more important for recruitment or performance management?
Job analysis is equally important for both recruitment and performance management. It ensures effective talent acquisition by accurately defining job requirements, and it provides a foundation for performance management by establishing clear job expectations and performance metrics.
Conclusion
Job analysis is an essential process in human resource management that enables organizations to understand and define job requirements, establish effective HR practices, and align talent with job roles. It helps organizations enhance recruitment and selection processes, improve performance management, support training and development initiatives, enable fair compensation strategies, and optimize job designs.