Introduction to Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning is a strategic process that involves systematically forecasting an organization’s future workforce needs and planning the necessary actions to ensure the availability of skilled and competent employees.
This proactive approach enables organizations to effectively manage their human resources, align them with organizational goals, and adapt to the rapidly changing business environment. By identifying and addressing potential workforce gaps and challenges, HRP plays a crucial role in maximizing organizational success.
Human Resource Planning Definition
Define human resource planning?
Human Resource Planning, often abbreviated as HR planning, refers to the strategic process through which an organization anticipates, identifies, and plans for its current and future human resource needs in order to effectively achieve its goals and objectives.
It involves assessing the organization’s workforce requirements, analyzing the existing workforce’s skills and capabilities, and formulating strategies to ensure that the right people with the right skills are available at the right time and in the right positions.
HR planning encompasses various aspects, such as recruitment, training, development, retention, and succession planning, all aimed at aligning the organization’s human resources with its overall strategic direction. This process helps organizations proactively address potential skill gaps, manage workforce fluctuations, and maintain a competitive advantage in the ever-changing business environment.
Table of Contents
Key Elements of HRP
Workforce Demand Forecasting
Accurate workforce demand forecasting is crucial for ensuring the right number of employees with the right mix of skills at the right time. It involves quantifying the organization’s future labor needs based on factors such as anticipated business growth, market conditions, technological advancements, and changes in customer demands.
Techniques such as trend analysis, predictive modeling, and scenario planning can be used to enhance the accuracy of demand forecasting. By aligning HR policies and programs with future demand, organizations are better equipped to meet their staffing requirements and avoid potential talent shortages or surpluses.
Workforce Supply Analysis
Workforce supply analysis focuses on assessing the current capabilities and competencies of the workforce and identifying potential skill gaps and shortages.
This analysis involves evaluating internal talent pools, reviewing succession planning strategies, and considering external factors such as demographic trends, labor market conditions, and industry-specific talent availability.
By understanding the existing talent landscape, organizations can develop targeted recruitment and development strategies to address any identified gaps and ensure a steady supply of skilled employees.
Gap Analysis and Succession Planning
Gap analysis plays a crucial role in identifying discrepancies between the organization’s current workforce capabilities and its desired future state. By analyzing the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the workforce, HR professionals can identify skill gaps, surplus or shortages of employees, and areas where succession planning is needed.
Strategies for bridging skill gaps may include training and development programs, performance management initiatives, and strategic recruitment efforts. Additionally, effective succession planning ensures a smooth transition of leadership roles and critical positions, mitigating potential disruptions caused by retirements, resignations, or unexpected departures.
Recruitment and Selection Strategies
Job Analysis and Competency Mapping
Job analysis is a systematic process of gathering and analyzing information about a particular job’s required tasks, responsibilities, and qualifications. By conducting a thorough job analysis, HR professionals can identify the key job requirements to inform recruitment and selection strategies.
Competency mapping evaluates the skills and competencies needed for each job role and creates a framework for aligning workforce capabilities with organizational objectives. This approach ensures that the recruitment process is focused on attracting candidates with the required qualifications and competencies, contributing to a more efficient and effective selection process.
Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
Creating an attractive employer brand is essential for attracting and retaining top talent. Organizations need to position themselves as desirable employers by highlighting their unique culture, values, employee benefits, and opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Innovative recruitment strategies, such as leveraging social media platforms, networking events, and employee referral programs, can help organizations connect with potential candidates.
Furthermore, effective employee retention techniques, including competitive compensation packages, flexible work arrangements, and career development opportunities, can enhance employee engagement and reduce turnover rates.
Training and Development Programs
Identifying Training Needs
Identifying the training needs of employees is a crucial step in ensuring their continued growth and development. This process involves assessing skill gaps, knowledge deficiencies, and performance weaknesses.
Performance appraisals play a significant role in identifying areas where training is required. By collecting data through performance evaluations, employee feedback, and self-assessment surveys, organizations can gain valuable insights into the specific training needs of their workforce.
Designing Effective Training Programs
Once the training needs have been identified, designing effective training programs involves setting clear objectives and goals. These objectives should be aligned with the organization’s overall strategic objectives and address specific skill gaps or knowledge deficiencies.
HR professionals need to select appropriate training methods and techniques, such as workshops, seminars, e-learning platforms, or on-the-job training, based on the nature of the training requirements.
Evaluating the effectiveness of training programs through assessments, feedback, and performance reviews is vital to ensure continuous improvement and maximize the return on investment in training initiatives.
Performance Management and Appraisal
Establishing Performance Standards
Establishing clear performance standards is essential for ensuring that employees have a clear understanding of what is expected from them. By setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) performance goals, organizations can provide employees with a roadmap for success.
These performance standards should be aligned with both individual and organizational goals to create a culture of accountability and performance excellence.
Performance Appraisal Methods
Traditional performance appraisal methods, such as annual reviews, are often being replaced with more modern approaches. One such approach is the use of 360-degree feedback, where multiple perspectives, including feedback from supervisors, peers, subordinates, and even customers, are taken into account.
This enables a more holistic view of an employee’s performance. However, organizations need to be mindful of biases in performance appraisal and implement strategies to minimize their impact. Regular feedback, coaching, and support should be provided to employees to foster continuous improvement and growth.
Employee Engagement and Motivation
The Role of Employee Engagement
Employee engagement refers to the emotional commitment and dedication employees have towards their work and organization. It is crucial for enhancing productivity, job satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
Understanding the concept of employee engagement involves creating a work environment that fosters trust, open communication, and meaningful employee involvement.
Regular measurement and monitoring of employee engagement levels through surveys, focus groups, or interviews allows organizations to identify areas of improvement and implement strategies to foster a highly engaged workforce.
Motivating Employees for High Performance
Several theories of motivation, such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s two-factor theory, provide insight into what drives individuals to perform at their best. Organizations must implement motivational strategies that align with the unique needs and preferences of their employees.
This can include providing challenging work assignments, opportunities for growth and advancement, recognition and rewards for exceptional performance, and creating a supportive and inclusive work environment that fosters collaboration and teamwork.
Nature of Human Resource Planning
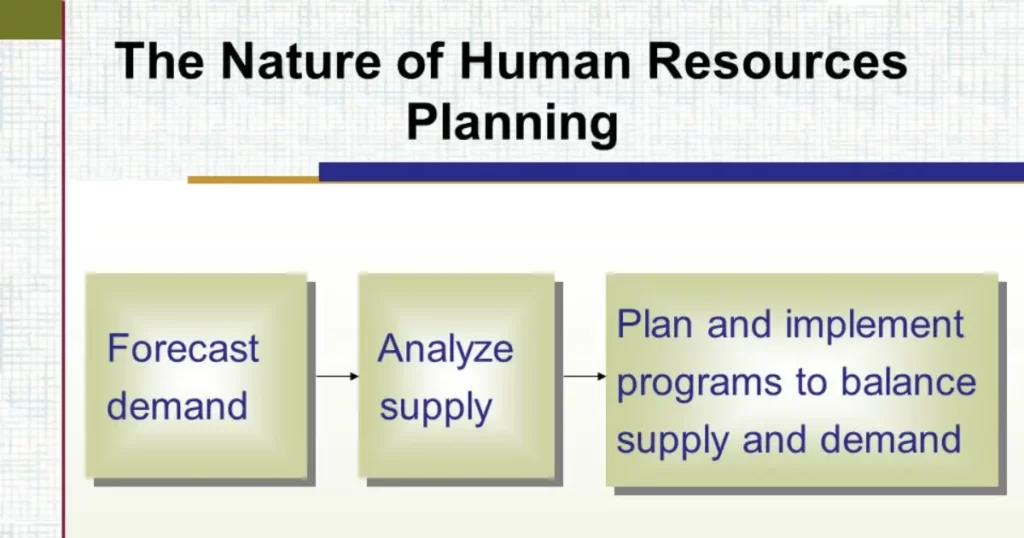
Forecasting demand
Forecasting demand in Human Resource Planning (HRP) is a critical step that involves predicting an organization’s future workforce needs to ensure that it has the right number of employees with the appropriate skills to meet its objectives.
By combining quantitative and qualitative methods and considering internal and external factors, organizations can develop more accurate forecasts of their future workforce demands. These forecasts serve as the foundation for effective human resource planning and help organizations meet their staffing needs efficiently.
Analyzing the supply
Analyzing the supply of human resources in Human Resource Planning (HRP) involves assessing the availability of current and potential employees both within and outside the organization. This analysis is crucial for matching workforce supply with demand to ensure that the right talent is available when needed.
Analyzing workforce supply is a dynamic process that requires regular updates to account for changing conditions in the labor market and within the organization. It is a critical component of HRP to ensure that an organization has the right talent available to meet its current and future needs effectively.
Balancing supply and demand
Balancing supply and demand in Human Resource Planning (HRP) involves developing and implementing programs and strategies that ensure the right quantity and quality of talent are available to meet an organization’s workforce needs.
Balancing supply and demand in HRP is an ongoing and dynamic process that requires proactive strategies and a commitment to talent development and management. By implementing these programs, organizations can ensure they have the right people with the right skills in the right positions to achieve their goals.
Importance of Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning is a crucial process that involves anticipating an organization’s future manpower needs and ensuring that it has the right people with the right skills in the right positions at the right time. The importance of human resource planning can be understood through several key points:

1. Talent Acquisition and Recruitment Efficiency: Effective human resource planning enables organizations to identify their future workforce requirements and proactively initiate recruitment processes. This ensures that there is a steady supply of qualified candidates available to fill vacant positions, reducing recruitment lead times and ensuring the selection of suitable candidates.
2. Strategic Alignment: Human resource planning aligns with an organization’s overall business strategy. By identifying the skills and competencies needed to achieve strategic goals, HR can focus on developing and acquiring talent that will drive the organization forward.
3. Employee Development and Training: With a clear understanding of future skill requirements, human resource planning facilitates the identification of training and development needs. This ensures that employees are equipped with the necessary skills to take on new challenges and responsibilities, contributing to their professional growth and the organization’s success.
4. Succession Planning: Organizations can identify potential future leaders and critical roles through human resource planning. This enables them to groom and prepare internal candidates for key positions, reducing the risk of leadership gaps and disruptions caused by sudden departures.
5. Cost Control: Efficient human resource planning minimizes labor shortages and surpluses. Avoiding overstaffing reduces unnecessary labor costs, while preventing understaffing helps avoid the costs of decreased productivity, overtime, and potential burnout.
6. Flexibility and Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, human resource planning allows organizations to adapt to new technologies, market shifts, and industry trends by aligning their workforce with evolving needs.
7. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Human resource planning ensures that an organization’s workforce complies with labor laws, regulations, and diversity and inclusion requirements. This helps mitigate legal risks and promotes a fair and inclusive workplace.
8. Employee Morale and Engagement: When employees see that the organization is invested in their growth and development, it boosts morale and job satisfaction. Transparent communication about career paths and opportunities fosters a sense of loyalty and commitment.
9. Effective Performance Management: By linking job roles, responsibilities, and competencies to the organization’s goals, human resource planning supports the development of effective performance management systems that align individual and team objectives with the overall strategy.
10. Long-Term Sustainability: A well-structured human resource planning process contributes to the long-term sustainability of an organization. It helps manage demographic shifts, retirements, and generational changes in the workforce, ensuring continuity and stability.
Emerging Trends in HRP
Technology and HR Planning
The rapid advancement of technology, including artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, is transforming HR processes and practices. HR professionals can leverage HR analytics to gather and analyze data for data-driven decision-making, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of HRP initiatives.
Additionally, the rise of virtual workforces and remote work arrangements are reshaping the way organizations operate. HR professionals must adapt their planning strategies to accommodate these trends and effectively manage virtual teams while ensuring employee engagement and performance.
Diversity and Inclusion in HR Planning
Acknowledging the value of diversity and inclusion is essential for enhancing organizational performance and fostering innovation. HR planning should embrace diversity by implementing inclusive strategies and policies that promote equal opportunities, eliminate biases, and create an inclusive work culture.
By enhancing diversity in the workforce, organizations can tap into a broader range of perspectives, experiences, and talents, driving creativity, problem-solving, and overall business success.
Human Resource Planning Process
The Strategic Human Resource Planning process involves several key steps that organizations follow to align their human resource management practices with their overall business strategy. Here are the typical steps for human resource planning in the process: The first step of human resource planning is;
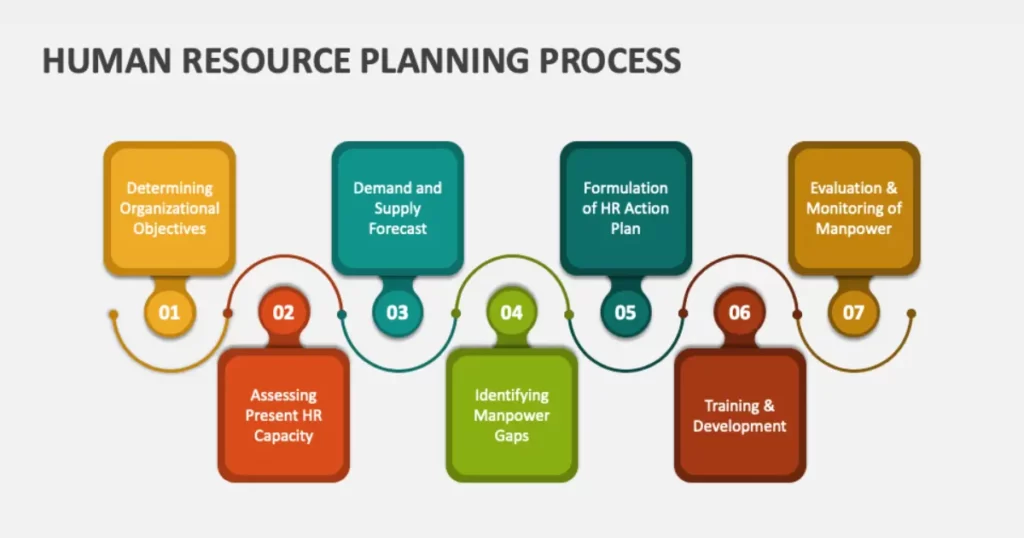
The first step in the human resource planning process is;
Environmental Analysis:
- Identify and analyze external factors that could impact the organization’s human resource needs, such as economic trends, industry changes, technological advancements, and demographic shifts.
- Assess internal factors, including the organization’s mission, vision, goals, and current workforce capabilities.
Demand Forecasting:
- Estimate the future workforce requirements based on the organization’s growth projections, expansion plans, and changes in business activities.
- Consider factors like new projects, market demands, and potential turnover.
Supply Analysis:
- Evaluate the current workforce’s skills, capabilities, and demographics.
- Identify gaps between the existing workforce and the future requirements, focusing on skills shortages or surpluses.
Gap Analysis:
- Compare the demand forecast with the supply analysis to identify gaps in the workforce’s quantity and quality.
- Determine which areas require immediate attention to address skill gaps or avoid overstaffing.
Developing HR Strategies:
- Based on the gap analysis, formulate HR strategies to address the identified gaps.
- Create plans for recruitment, training, development, and retention to ensure the availability of the right talent at the right time.
Implementation:
- Execute the HR strategies by recruiting new employees, providing training programs, and implementing retention initiatives.
- Monitor progress and make necessary adjustments as circumstances change.
Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Continuously assess the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and their impact on workforce alignment with business goals.
- Collect feedback from managers, employees, and stakeholders to refine the strategies.
Feedback Loop and Adjustments:
- Incorporate feedback and lessons learned into future HR planning cycles.
- Adjust strategies as needed to ensure that the organization remains adaptable to changing business conditions.
Integration with Business Strategy:
- Ensure that HR planning is closely integrated with the overall organizational strategy.
- Align HR initiatives with the broader business objectives to maximize the impact of human capital on achieving organizational goals.
Succession Planning and Talent Development:
- Identify key positions within the organization and develop plans for grooming internal talent to fill these positions in the future.
- Invest in employee development and training programs to enhance skills and leadership capabilities.
Conclusion
HR Planning plays a crucial role in future-proofing organizational success by aligning HR strategy with organizational goals, understanding the strategic context, analyzing workforce demand and supply.
Implementing effective recruitment and selection strategies, designing training and development programs, managing performance and appraisal.
Fostering employee engagement and motivation, managing workforce change, and adapting to emerging trends. By proactively planning for their human resources, organizations can ensure they have the right people with the right skills at the right time, leading to sustainable and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why Human Resource Planning is important for business growth?
HR Planning is important for business growth as it ensures that organizations have the necessary human capital to support their strategic objectives and respond to changing business needs. It helps in identifying talent gaps, attracting and retaining top performers, and developing succession plans to ensure a steady pipeline of skilled employees.
2. How can organizations align HR strategy with their overall goals?
Organizations can align HR strategy with their overall goals by first clearly defining their goals and objectives. HR professionals can then develop HR policies and programs that support these goals, such as talent acquisition and retention strategies, training and development initiatives, and performance management systems that focus on the organization’s strategic priorities.
3. What are the main challenges in workforce demand forecasting?
Workforce demand forecasting faces challenges such as uncertainty in future business conditions, changing market dynamics, and technological advancements that may disrupt traditional roles and workforce requirements. Additionally, external factors such as economic fluctuations and regulatory changes can impact accurate demand forecasting.
4. How can HR effectively bridge skill gaps through training and development?
HR can effectively bridge skill gaps by conducting a thorough training needs analysis, identifying specific areas of improvement, and developing targeted training programs. By selecting appropriate training methods and techniques and regularly evaluating the effectiveness of these programs, HR can enhance employees’ skills and competencies to bridge the identified gaps.
5. What are some modern performance appraisal methods?
Modern performance appraisal methods include 360-degree feedback, where feedback is sought from multiple sources, and continuous feedback systems that encourage ongoing conversations between managers and employees. These approaches provide a more comprehensive and holistic assessment of an employee’s performance, contributing to a more accurate evaluation and development process.
6. How can organizations promote employee engagement and motivation?
Organizations can promote employee engagement and motivation by creating a supportive and inclusive work environment that fosters collaboration, trust, and open communication. Implementing motivational strategies, such as providing challenging work assignments, growth opportunities, and recognition for exceptional performance, can also enhance employee engagement and motivation.
7. What strategies can HR employ during workforce restructuring?
During workforce restructuring, HR can employ strategies such as effective communication to ensure employees understand the reasons for change, providing resources and support to affected employees, and offering outplacement services or career counseling. HR should prioritize transparency, fairness, and compassion throughout the restructuring process.
8. What role does technology play in HR planning?
Technology plays a significant role in HR planning by enabling HR professionals to gather and analyze data for decision-making, automate routine HR processes, and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of HR initiatives. HR analytics and digital platforms enhance the accuracy of workforce forecasting, talent management, and performance evaluation.
9. Why is diversity and inclusion important in HR planning?
Diversity and inclusion are important in HR planning as they contribute to organizational performance and innovation. Embracing diversity creates a workforce that reflects the diversity of our society, promotes equal opportunities, and nurtures a culture of belonging. It allows organizations to access a broader range of ideas and perspectives, leading to enhanced problem-solving and better decision-making.
10. How does HR planning contribute to organizational adaptability?
HR planning enables organizations to anticipate and adapt to the ever-changing business environment by ensuring the availability of skilled and competent employees. By identifying potential workforce gaps, implementing training and development programs, and fostering employee engagement and motivation, HR planning enhances organizational adaptability and resilience.